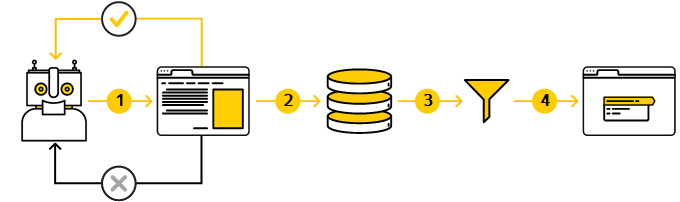
How does Yandex search work?
To start displaying your site in search results, Yandex must find out about its existence using the robots.
A robot is a system that crawls site pages and loads them into its database. Yandex has lots of robots. Saving pages to the database and their further processing using algorithms is called indexing. Based on the uploaded data, search results are generated. They are regularly updated and may affect the site ranking.
There are several stages before a site appears in search results:
Stage 2. Loading and processing (indexing) the data
Stage 3. Creating a database of the pages that can be included in search results
Stage 4. Generating search results
Stage 1. Crawling the site
The robot determines which sites to crawl and how often, as well as how many pages to crawl on each of them.
When crawling them, the robot takes into account the list of already known pages, which is based on the following data:
- Internal and external links.
- Links specified in the Sitemap file.
- Yandex Metrica data.
- Directives in the robots.txt file.
- The site page size — pages larger than 10 MB are not indexed.
Robots continually monitor the appearance of new links, content updates on previously downloaded pages, and page availability. They do this as long as:
- The link is placed on your own or third-party site.
- The page is not prohibited for indexing in the
robots.txtfile.
When the robot tries to load a site page, it receives a response from the server with the HTTP status code:
|
HTTP status code |
Note |
|
200 OK |
The robot will crawl the page. |
|
The robot needs to crawl the page that is the redirect target. Learn more about handling redirects. |
|
|
A page with this code won't be included in the search. If it was before the robot crawled it, then it will be removed from the search. To prevent the page from falling out of the search, configure the server so that it responds with the 429 code. The robot will access the page and check the response code. This can be useful if the site page looks incorrect due to problems with the CMS. After the error is fixed, change the server response. Note If the page responds with the 429 code for a long time, it will indicate that the server experiences difficulties with the load. This can reduce the site crawl rate. |
Useful tools
- Troubleshooting — Helps check the quality of a site and fix errors, if any.
- Crawl statistics — Shows which pages the robot crawled and how often it accesses the site.
- How to reindex a site — Allows you to report a new page on the site or an update of a page already included in the search.
- Region — Helps the robot to correctly determine the region of the site and display it for location-dependent queries.
- Server response check — Indicates whether the page to be indexed is accessible to the robot.
HTTP/2 version support
-
The Yandex indexing bot supports HTTP/2. The HTTP/2 protocol speeds up page loading, including on mobile devices, which makes it easier for users to interact with the website. On top of that, this protocol reduces server load and saves traffic. The HTTP/2 protocol doesn't directly affect the frequency of crawling a website and doesn't change the website's position in Yandex search results.
If you use HTTP/1.1, the robot will continue indexing your website. These two protocols are compatible, so there will be no conflicts with your server settings.
Stage 2. Loading and processing (indexing) the data
The robot determines the content of the page and saves it to its database. To do this, it analyzes the page content, for example:
- The contents of the description meta tag, the title element, and the Schema.org markup, which can be used to generate a page snippet.
- The noindex directive in the
robotsmeta tag. If it's found, the page won't be included in the search results. - The rel="canonical" attribute indicating the address that you consider a priority for displaying in the search results for a group of pages with the same content.
- Text, images, and videos. If the robot determines that the content of several pages matches, it may treat them as duplicates.
Recommendations
Useful tools
- Troubleshooting — Helps check the quality of a site and fix errors, if any.
- Crawl statistics — Shows which pages the robot crawled and how often it accesses the site.
- How to reindex a site — Allows you to report a new page on the site or an update of a page already included in the search.
Stage 3. Creating a database of the pages that can be included in search results
Based on the information collected by the robot, the algorithms determine the pages that can be included in the search results. The algorithms take into account a variety of ranking and indexing factors that are used to make the final decision. For example, the database won't include pages with indexing disabled or duplicate pages.
A page may contain the original, structured text but the algorithm won't add it to the database, as it's highly unlikely that the page gets into the range of view in the search results. For example, due to lack of demand from users or high competition in this topic.
Useful tools
- Pages in search — Helps you track the status of site pages, for example, HTTP response status codes or duplicate pages.
- Site security — Provides information about violations and infected files.
To find out if a site subdomain appears in the search results, subscribe to notifications.
Stage 4. Generating search results
The algorithm determines the quality of a page, namely:
- To what extent the page content matches the search query (i.e., whether it's relevant).
- Whether the page content is clear and useful to the user.
- Whether the page is convenient (how text is structured, paragraphs and headers of different levels are arranged, and so on).
If the page quality is high enough, it's more likely that it will be included in the search results. As a result, not all site pages appear in Yandex search. They may also disappear from the search results.
How to improve site ranking in search results
Useful tools
- Pages in search — Allows you to find out which site pages are included or excluded from the search results. You can also track pages that are most important to you.
- Query statistics — Helps you track the number of impressions of your site and clicks on the snippet.
- All queries and groups — Shows the search queries for which your site is displayed in the search results.
- Troubleshooting — Provides information about the pages that have no description meta tag or title element.
- Sitelinks — Helps you check if there're sitelinks in the snippet and configure them.
Questions and answers
The page description in the snippet differs from the content in the description meta tag
The page description in the search results is based on the text that is most relevant to the search query. This can be the content of the Description meta tag or the text placed on the page. For more details, see the Snippet section.
Search results show links to internal site frames
Before loading the page in the browser console, check if the parent frame with navigation is open. If not, open it.
My server doesn't provide last-modified
Your site will still be indexed even if your server doesn't provide last-modified document dates. However, you should keep in mind the following:
-
The date won't be displayed in the search results next to your site pages.
-
The robot won't know if a site page has been updated since it was last indexed. Modified pages will be indexed less often, as the number of pages that the robot gets from a site each time is limited.
How does encoding affect indexing?
The type of encoding used on the site doesn't affect the site indexing. If your server doesn't pass the encoding in the header, the Yandex robot will identify the encoding itself.
Can I manage reindexing frequency with the Revisit-After directive?
No. The Yandex robot ignores it.
Does Yandex index a site on a foreign domain?
Yes. Sites containing pages in Russian, Ukrainian, and Belarusian are indexed automatically. Sites in English, German, and French are indexed if they might be interesting to users.
How does a large number of URL parameters and the URL length affect indexing?
A large number of parameters and nested directories in the URL, or overly long URLs, may interfere with the site indexing.
The URL can be up to 1024 characters.
Does the robot index GZIP archives?
Yes, the robot indexes archives in GZIP format (GNU ZIP compression).
Does the robot index anchor URLs (#)?
The Yandex robot doesn't index anchor URLs of pages, except for AJAX pages (with the #! character). For example, the http://example.com/page/#title page won't get into the robot database. It will index the http://example.com/page/ page (URL before the # character).
How does the robot index paginated pages?
The robot ignores the rel attribute with the prev and next values. This means that pagination pages can be indexed and included in search without any restrictions.
Learn more
- How do I make my site appear in search results?
- Why is it taking so long for pages to appear in search results?
- Why are pages excluded from the search?
- How many site pages are included in search?
A link that connects pages on a single site. Pages can be located in different directories of the same domain or on subdomains.
A link located on another site.
A query that is related to a specific region. For example, [taxi] or [buy iphone]. Learn more